Why do we get sensitive teeth?
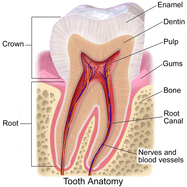
Sensitive teeth or a sensitive tooth can be caused by many different things. Each of your teeth has a blood and nerve supply which enters the tooth at its apex which is hidden at the end of the tooth root in your jawbone. The nerves feed information back to your brain about eating, chewing, clenching and more. Unfortunately there are lots of pain nerve fibres in your tooth. The nerve tissue is covered by the dentine which is less hard than enamel and is made up of lots of tunnels which are intimately connected to the nerve fibres and so this part of your tooth is sensitive. This is usually covered by the rock solid enamel which the nerve supply cannot penetrate.
As you can see therefore, anything that exposes the dentine of the tooth or otherwise irritates the nerves inside your tooth has the potential to cause tooth sensitivity or sensitive teeth.
Below are all the main causes of Sensitive teeth along with why they cause tooth sensitivity. The second table details how to treat each form of tooth sensitivity:
|
Cause
|
Why it causes sensitivity?
|
|
Recent deep filling in your tooth
|
The filling may be very deep and it may take a while for the inflamed nerve beneath it to settle down. This will often be hypersensitive to cold and sweet foods and drinks. Alternatively the nerve may never settle down and may lead to toothache and the need for a root canal treatment or extraction.
|
|
Recent high filling or other restoration in/on your tooth
|
This will often be felt as a high spot on your tooth when biting and will cause pain or sensitivity when biting down or chewing as soon as the numbness (if you had local anaesthetic) has worn off.
|
|
Leaking filling
|
This may be an old filling that has decay around the edges or a new filling that has not bonded or been packed fully into place. This will be sensitive to cold and sweet and often sensitive to sucking cold air in.
|
|
Tooth Decay
|
Tooth decay can often go unnoticed as it generally doesn't cause sensitivity or pain until it has progressed a long way into your tooth. At this point your tooth will become hypersensitive to cold and sweet foods and drinks and eventually sensitive to bite on.
|
|
Lost filling, crown or other restoration
|
If your tooth has not been root treated then often losing a filling or other restoration exposes the dentine which is the sensitive part of the tooth. Unless covered this will by hypersensitive to hot, cold and sweet.
|
|
Cracked tooth
|
This is a specific type of pain where you will get sensitivity to cold and sweet foods depending on the extent of the crack. You will also get pain after biting when you release from biting. i.e. if you clench it will not be sore but once you then unclench your teeth it will start to be sore.
|
|
Trauma
|
Any trauma to teeth that exposes the dentine i.e. on the front incisors usually anything more than a 2mm fracture will cause the tooth or teeth to be sensitive to cold and sweet foods
|
|
Gum recession
|
Gum recession may occur as a result of gum disease, brushing too hard, ageing or a number of other reasons. The dentine of the tooth below gum level is usually covered by bone and gum but as the bone and gum recedes it slowly exposes the sensitive dentine underneath. This will usually be generalised around the whole mouth but can be localised to one or more teeth.
|
|
Tooth wear from grinding
|
Tooth wear from grinding (bruxism) will wear away the protective enamel as well as cause little enamel fractures at the gum level. This will expose sensitive dentine underlying the enamel which can cause generalised tooth sensitivity. You may have associated jaw pain or jaw-ache as a result of clenching and grinding also.
|
|
Acid Erosion
|
This is another form of wear caused by a diet that is too acidic i.e. too much citrus fruit, sugar, fizzy drinks and so on. The acidity will erode away the enamel on teeth hence exposing the sensitive underlying dentine and causing generalised sensitivity. If you have reflux or you vomit regularly it can cause acid erosion also which can lead to tooth sensitivity and tooth decay.
|
|
gum disease and periodontal disease
|
This causes inflamed gums which are held away from the teeth, as a result there is no longer a tight seal around the neck of the teeth and the sensitive underlying dentine is exposed. Chronic periodontitis also leads to accelerated gum recession and often generalised sensitivity of the affected teeth.
|
|
Tooth whitening, whether done at home or in the surgery has the potential to cause temporary tooth sensitivity. If you are having tooth whitening done then your gums need to be in perfect condition beforehand and you should use desensitising toothpaste before, throughout and afterwards to reduce the potential for tooth sensitivity.
|
Sensitive Teeth Treatment
|
Cause
|
Home Treatment
|
Dentist Treatment
|
|
Recent deep filling in your tooth
|
May monitor for a few weeks but if not improving or if worsening then need to see the dentist as soon as possible.
|
If not improving then dentist may need to medicate your tooth and refill it at a later date or carry out a root canal treatment or extraction.
|
|
Recent high filling or other restoration in/on your tooth
|
May monitor for a couple of weeks to see if it settles but if it does not then see the dentist as soon as possible.
|
Your dentist will adjust the biting surface of the restoration until it feels comfortable to bite and chew on.
|
|
Leaking filling
|
Call your dentist to arrange an appointment and in the meantime, use sensitive toothpaste such as "Sensodyne Pronamel" or any of the other well known branded sensitive toothpastes
|
Your dentist can replace the filling or sometimes repair the filling where it is leaking. It may be best to have a white filling as these can bond to the tooth to seal the dentine whereas amalgam fillings cannot.
|
|
Tooth Decay
|
Arrange to see dentist and reduce sugar in your diet. Ensure tooth brushing effectively and ensure to be using floss regularly to help prevent decay between your teeth
|
See your dentist to have the decay removed and the tooth or teeth restored. If your tooth is unrestorable it may require extraction
|
|
Lost filling, crown or other restoration
|
Arrange an appointment with the dentist, In the meantime you may purchase a temporary filling kit from a pharmacy or some supermarkets to help cover over any sensitive cavities.
|
See dentist at earliest convenience so as they can assess the problem and treat it accordingly.
|
|
Cracked tooth
|
Avoid biting anything hard with the tooth and take ibuprofen painkillers if you are allowed (avoid them if you have any stomach issues) and arrange to see your dentist as soon as possible.
|
The dentist will investigate the crack and often will numb the tooth and remove the crack and any fillings. Sometimes the crack goes through the entire tooth and it needs extracting. Other times the crack will be small and can be treated with an adhesive white filling.
|
|
Trauma
|
Call dentist (or A&E if severe) and get seen as quickly as possible for the best chance of successful treatment. Take painkillers while you are waiting to be treated.
|
The dentist will temporarily repair any broken teeth that are sensitive, remove any exposed nerves and often splint (join) teeth with white filling material to help stabilise them.
|
|
Gum recession
|
If generalised and ongoing then sensitivity from gum recession can be treated with regular use of desensitising toothpaste such as "Sensodyne Pronamel" or other branded sensitive toothpastes. Avoid brushing too hard and ensure to be using either a soft manual toothbrush or an electric toothbrush that is simply held on the tooth and not used to scrub.
|
May be treated with "duraphat" prescription toothpaste which is a lot stronger than those bought over the counter. Your dentist may apply sealant to the tooth or fluoride varnish to help tackle the sensitivity. They may sometimes place small white or pink fillings to seal the sensitive exposed dentine also.
|
|
Tooth wear from grinding
|
See dentist as soon as possible, distraction techniques and sensitive toothpaste can be used. We would advise against wearing a normal mouthguard as it is not close fitting and may affect teeth by allowing some to over-erupt whilst others are in the guard.
|
Your dentist can make a soft splint (mouthguard) to wear at night or in the day in order to prevent further wear. Again they may give prescription toothpaste to help with generalised sensitivity. If severe they can restore your teeth with adhesive white fillings and crowns.
|
|
Acid Erosion
|
Reduce acidic foods and drink in the diet, use sensitive toothpaste regularly. Don;t brush straight after acidic foods and drinks; ideally rinse with water in between acidic food and drink and tooth brushing. Use a soft manual toothbrush or an electric toothbrush with gentle brushing technique.
|
Oral hygiene and diet advice at the dentist, prescription toothpaste to help with generalised sensitivity. Restoring worn surfaces with adhesive white composite restorations or adhesive lab made crowns and onlays. Prescription of anti-acids such as Omeprazole to prevent acid reflux.
|
|
Gum disease and periodontal disease
|
Improve oral hygiene, improve tooth brushing and ensure to be using dental floss or other interdental cleaning aids. Stop smoking, use sensitive toothpaste
|
If gum disease (gingivitis) then improved tooth brushing should reverse it. If periodontitis (your dentist will be able to tell you which you have) then it will need gum treatment with the dentist or hygienist as well as other methods of desensitising such as prescription toothpaste and fluoride varnish.
|
|
Tooth whitening
|
Use of sensitive toothpaste, reduced acidic foods such as citrus fruits, fizzy drinks and sweets; especially during the tooth whitening period. Limit the whitening so as you are not doing home whitening every night for example but every other night instead or less frequently depending on severity of sensitivity.
|
Your dentist may give you prescription toothpaste to use during whitening. All gum treatment is to be completed to ensure healthy gums prior to commencing whitening. Any leaking fillings, broken teeth and any of the above issues are treated before commencing tooth whitening.
|
As an additional note, If you have crowded or crooked teeth then your risk of tooth decay, gum disease and trauma may be increased and therefore your risk of tooth sensitivity. It may be wise to seek orthodontic treatment not only to improve the appearance of your teeth but to improve their function and reduce your risk of tooth decay, gum disease, trauma and sensitive teeth.
We hope you found this information useful and remember, any further questions you can always ask our dentists by clicking below or ask your own dentist of course...
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed